Telemedicine apps are revolutionizing healthcare by providing convenient and accessible medical care from the comfort of your own home. With a myriad of features and functionalities, these apps are transforming the way we access healthcare services, improving outcomes, and empowering patients.
From virtual consultations and remote monitoring to prescription management and health tracking, telemedicine apps offer a wide range of services that cater to diverse patient needs. Their user-friendly interfaces and secure platforms make them an ideal solution for those seeking convenient, affordable, and personalized healthcare.
Definition and Scope of Telemedicine Apps

Telemedicine apps provide a virtual platform for healthcare professionals and patients to interact remotely. These apps facilitate virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and access to medical information.
Common Features and Functionalities
- Video and audio conferencing for virtual consultations
- Messaging and chat features for patient-provider communication
- Patient record management and sharing
- Remote monitoring of vital signs and health data
- Access to medical information and resources
Target Audience and Use Cases
Telemedicine apps cater to a wide range of users, including:
- Patients seeking convenient and accessible healthcare
- Healthcare professionals providing remote consultations
- Individuals in remote or underserved areas
- People with mobility or transportation challenges
Use cases for telemedicine apps include:
- Virtual doctor visits for routine checkups and consultations
- Remote monitoring of chronic conditions
- Telepsychiatry services
- Access to specialist care in remote areas
- Emergency medical consultations
Benefits and Advantages of Telemedicine Apps
Telemedicine apps offer a plethora of benefits and advantages, making them an increasingly popular healthcare solution. These apps enhance convenience, accessibility, and healthcare outcomes, leading to improved patient experiences and overall well-being.
One of the primary advantages of telemedicine apps is their convenience. Patients can access healthcare services from the comfort of their own homes, eliminating the need for time-consuming travel to a physical clinic. This is especially beneficial for individuals with mobility issues, those living in remote areas, or those with busy schedules.
Moreover, telemedicine apps improve accessibility to healthcare. They break down geographical barriers and provide access to specialized medical expertise that may not be readily available in a patient’s local area. This is particularly important for patients in rural or underserved communities who may have limited access to traditional healthcare facilities.
Improved Healthcare Outcomes
Telemedicine apps have also been shown to improve healthcare outcomes. By providing timely access to care, telemedicine can help patients manage chronic conditions, prevent complications, and receive early intervention for acute illnesses. This can lead to improved overall health, reduced hospitalizations, and lower healthcare costs.
For example, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that patients with diabetes who used a telemedicine app had better blood sugar control and lower HbA1c levels compared to those who received traditional in-person care.
Successful Use Cases and Patient Experiences
There are numerous successful use cases of telemedicine apps, demonstrating their effectiveness in improving healthcare delivery. For instance, the VA Telehealth Services program has been widely recognized for its success in providing remote care to veterans. The program has been shown to improve access to care, reduce costs, and enhance patient satisfaction.
Another example is the use of telemedicine apps in disaster response. During the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine played a critical role in providing care to patients while minimizing the risk of exposure to the virus. Telemedicine apps allowed healthcare providers to conduct virtual consultations, prescribe medications, and monitor patients remotely.
Challenges and Limitations of Telemedicine Apps
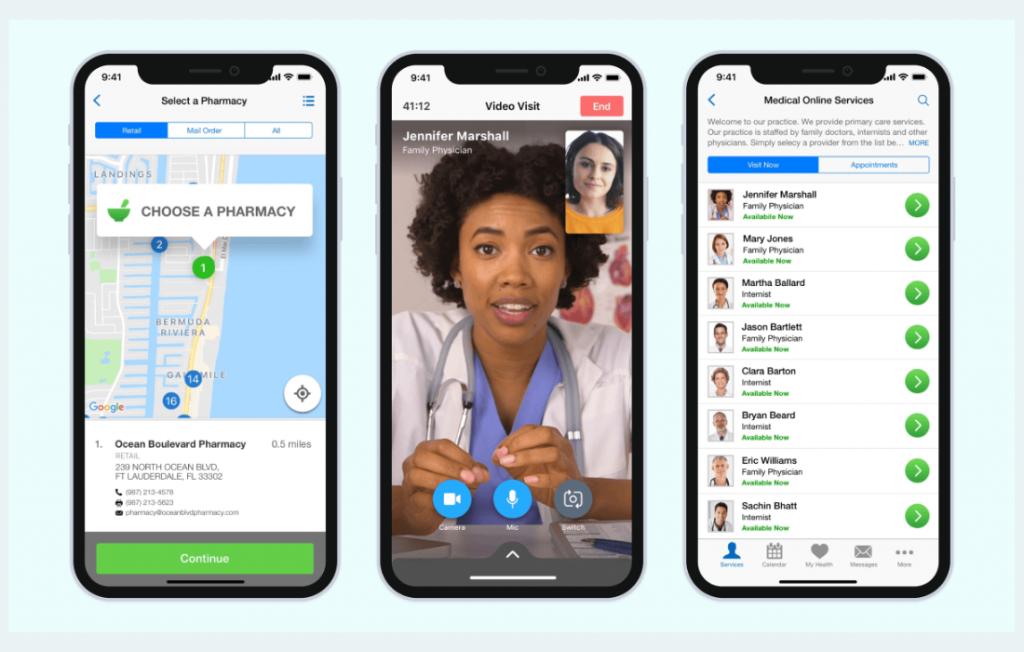
While telemedicine offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges and limitations. These include technological constraints, potential diagnostic and treatment limitations, and concerns regarding data security and privacy.
Technological Challenges
- Internet connectivity:Stable and high-speed internet connectivity is crucial for effective telemedicine consultations. However, this may not always be available in rural or remote areas.
- Device compatibility:Telemedicine apps require compatible devices, such as smartphones or tablets. However, not everyone has access to such devices or the necessary technical knowledge to use them.
- Audio and video quality:Poor audio and video quality can hinder communication and compromise the accuracy of diagnosis and treatment.
Limitations in Diagnosis and Treatment
- Physical examination:Telemedicine consultations lack the physical examination component, which can limit the accuracy of diagnosis for certain conditions.
- Emergency situations:Telemedicine apps are not suitable for emergency situations that require immediate medical attention.
- Complex medical conditions:Some complex medical conditions may require in-person consultations and advanced diagnostic tests that cannot be performed remotely.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
- Data breaches:Telemedicine apps store sensitive patient information, making them potential targets for data breaches.
- Data privacy:Patients may have concerns about the privacy of their medical information and its potential misuse.
- Regulatory compliance:Telemedicine apps must comply with various data security and privacy regulations, which can be complex and challenging to implement.
Design and Development Considerations for Telemedicine Apps
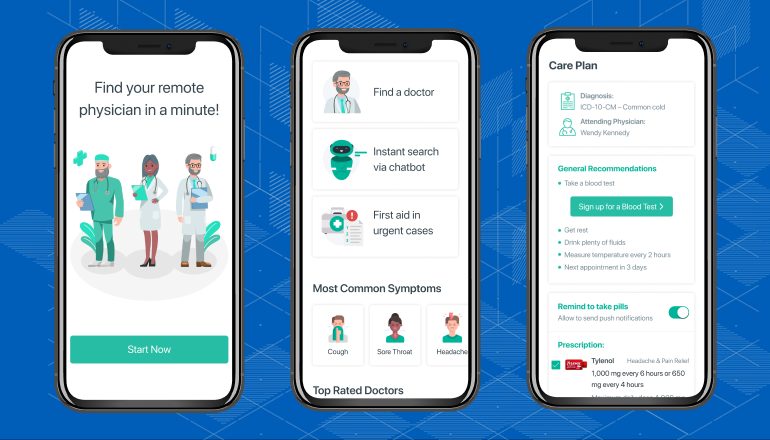
Telemedicine apps must prioritize user experience and technical security to facilitate effective healthcare delivery. Here are key considerations for designing and developing telemedicine apps:
Ensuring accessibility and inclusivity is crucial to cater to diverse user needs and promote equitable access to healthcare services.
User-friendly and Intuitive Design
- Use clear and concise language that is easily understandable by users with varying health literacy levels.
- Design intuitive navigation menus and user interfaces that allow users to find the desired features and information effortlessly.
- Provide visual cues and step-by-step instructions to guide users through the app’s functionality.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
- Ensure compatibility with assistive technologies such as screen readers and closed captioning for users with disabilities.
- Offer language translation options to accommodate non-native speakers.
- Consider cultural and socioeconomic factors to ensure the app is relevant and accessible to diverse populations.
Security and HIPAA Compliance, Telemedicine apps
- Implement robust security measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure data storage to protect patient data.
- Adhere to HIPAA regulations to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of protected health information.
- Regularly conduct security audits and updates to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Future Trends and Innovations in Telemedicine Apps
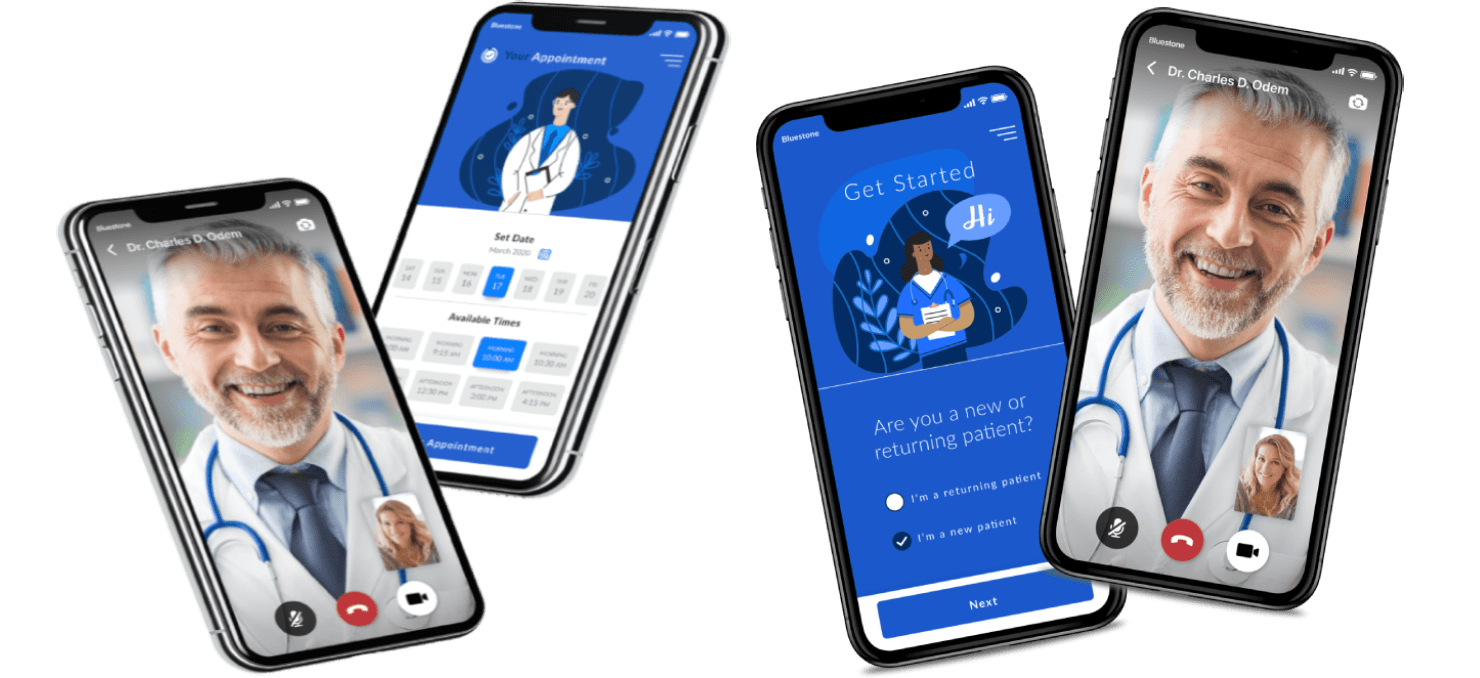
The future of telemedicine apps is bright, with emerging technologies poised to shape the landscape. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) hold immense potential to revolutionize telemedicine, enhancing patient care and streamlining healthcare delivery.
Impact of AI and ML in Telemedicine
AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data, including medical records, diagnostic images, and real-time health monitoring data. This enables the development of personalized treatment plans, early detection of diseases, and predictive analytics for risk assessment.
For example, AI-powered chatbots can provide personalized health guidance, answer patient queries, and triage symptoms. ML algorithms can analyze medical images to detect early signs of disease, enabling timely intervention and improving patient outcomes.
Transforming Healthcare Delivery Models
Telemedicine apps are transforming healthcare delivery models, making healthcare more accessible, convenient, and cost-effective. Remote patient monitoring allows healthcare providers to track patient health metrics from afar, enabling proactive care and early detection of health issues.
Virtual consultations empower patients to connect with healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes, reducing transportation barriers and improving access to specialized care. Telemedicine apps also facilitate remote prescribing and medication management, streamlining the process and improving patient adherence.
Concluding Remarks
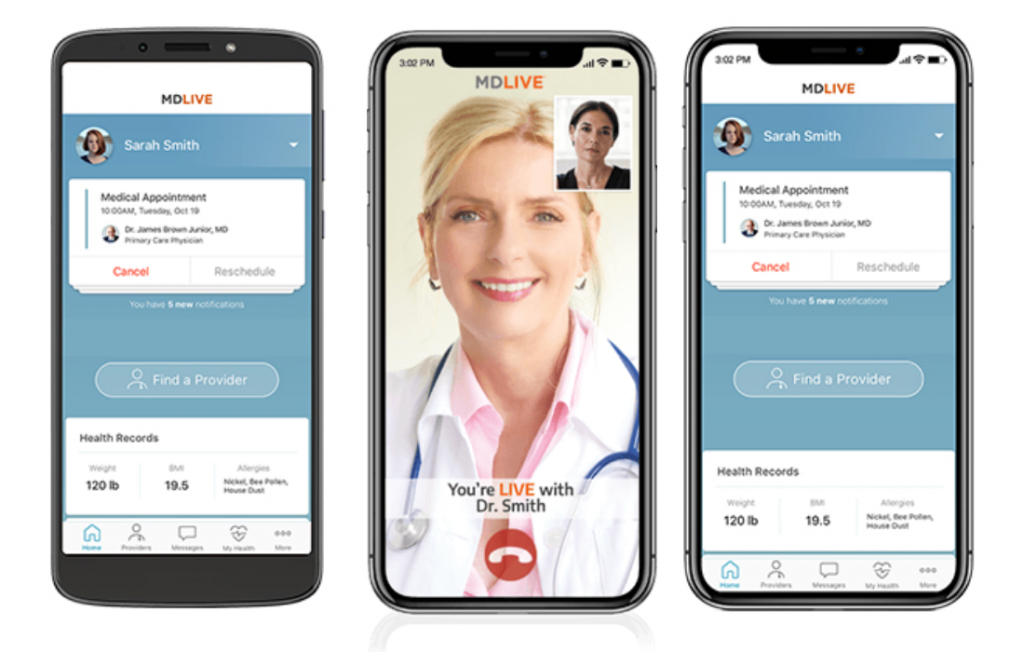
As technology continues to advance, telemedicine apps will undoubtedly play an even greater role in shaping the future of healthcare. With the potential for artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance diagnostic capabilities and personalized treatment plans, telemedicine apps are poised to revolutionize healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes on a global scale.
FAQ Summary
What are the benefits of using telemedicine apps?
Telemedicine apps offer numerous benefits, including convenience, accessibility, improved healthcare outcomes, reduced costs, and increased patient satisfaction.
Are telemedicine apps secure?
Yes, reputable telemedicine apps adhere to strict security protocols and HIPAA compliance to protect patient data and ensure privacy.
Who can use telemedicine apps?
Telemedicine apps are suitable for individuals of all ages and health conditions, providing accessible healthcare to those with limited mobility, busy schedules, or geographic barriers.